Wheel of SOURCING
Major Stages of Supply Chain Risk Management
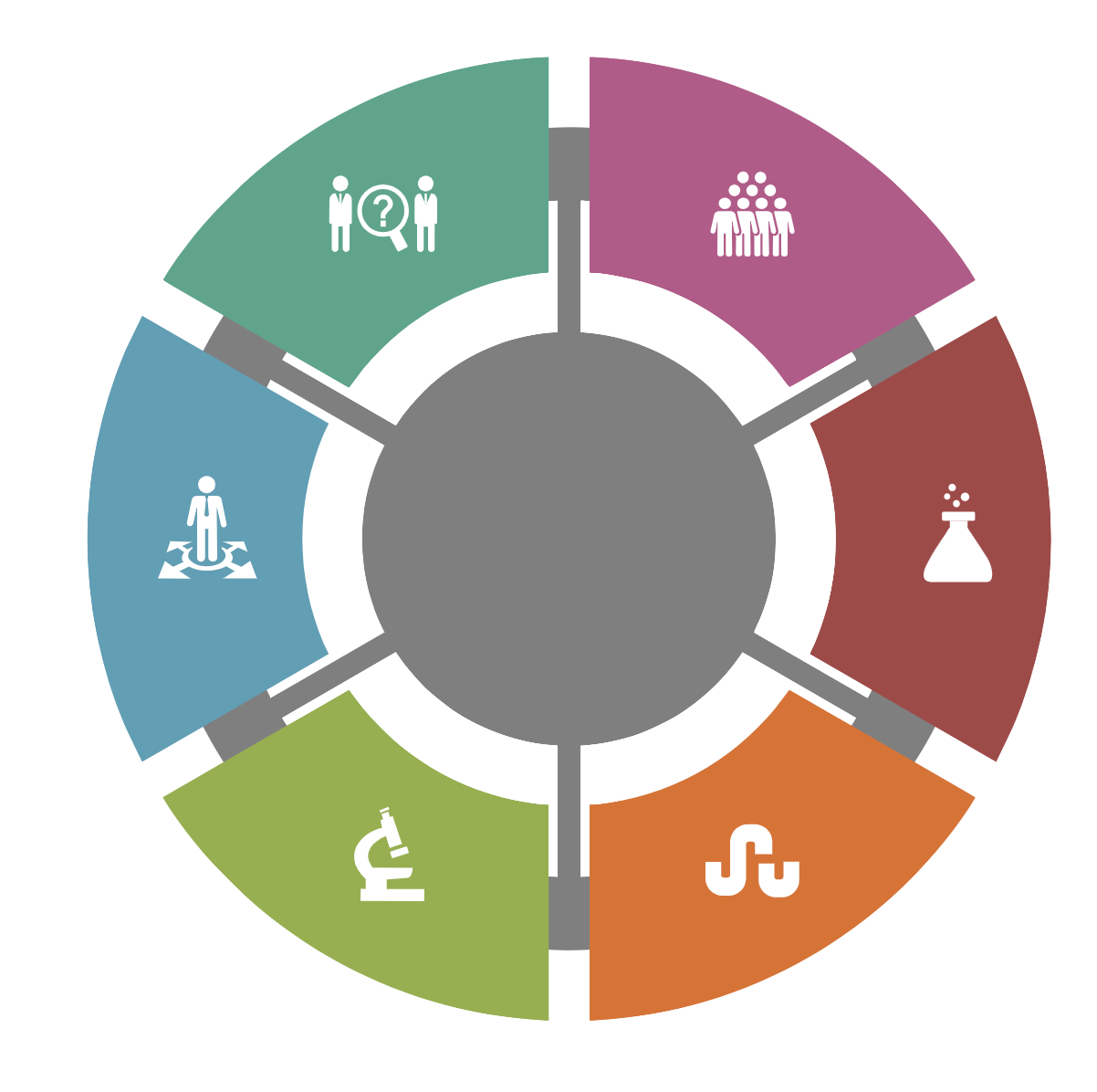
Major Stages of Supply Chain Risk Management
Before engaging on a significant acquisition or development of a new solution, it is important for the organization to develop a team to consider not only discrete business or operational requirements, but also to assess risks related to the organization, considering both the authorized or unauthorized use of the solution along with operational, financial, and regulatory risks. This will most likely require the formation of a multi-disciplinary team to include Legal, Sourcing, Business, and Information Security.
Cybersecurity Supply Chain Risk Management (C-SCRM) is a systematic process for managing exposures to cybersecurity risks, threats, and vulnerabilities throughout the supply chain and developing appropriate response strategies presented by the supplier, the supplied products, services, and the supply chain. Determine Qualifying Criteria. Perform Market Analysis. Models are available to assist entities identify and evaluate necessary supplier security practices. In addition, entities should consider methods to verify or certify the scope, strength, and efficacy of supplier practices..
Entities can choose from high-level measures using structured responses to a survey of 60 security criteria, use a questionnaire of 300 questions, or choose a hybrid approach based on an assessment of risk.
Entities can leverage a variety of existing tools to enumerate and manage risk using contractual mechanisms. Does the supplier support SBOM? What methods will the supplier use to integrate SBOM into their development process? What methods will the entity use to incorporate SBOM information into an overall risk management program?
Secure Delivery, add to the ongoing vulnerability management program. Certain high-risk components may be deserving of additional controls to manage risk associated with the delivery pathway from the assembly/manufacturing facility to the purchaser. Moreover, after the products are installed and integrated into operations, the entity using the products should consider methods to identify and mitigate new (or newly discovered) vulnerabilities
Ensure solution is retired/recycled in a manner to protect sensitive information/Environmentally Responsible Manner. It is helpful to consider the implications of retirement/cessation of the use of solutions. What methods will be used to neutralize sensitive PII or proprietary business information? Certain components may have sensitive operational or configuration information that should be eliminated. Entities should also consider the environmental impact of destruction/recycling options for components.